What is Inguinal Hernia?
Inguinal hernias are more common in men than women and can occur at any age. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, aging, chronic coughing or straining during bowel movements, heavy lifting, and pregnancy.
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia can include a bulge or lump in the groin area, pain or discomfort in the groin, especially when coughing or lifting, and a heavy or dragging sensation in the groin.
Treatment for an inguinal hernia typically involves surgery to repair the weakened abdominal wall and prevent the hernia from recurring. The two main types of surgery for inguinal hernia repair are open hernia repair and laparoscopic hernia repair, both of which involve reinforcing the weakened area of the abdominal wall with sutures or mesh.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have an inguinal hernia, as untreated hernias can lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, strangulation, and tissue damage.
Inguinal hernia surgery Benefits
Inguinal hernia repair surgery can offer several benefits, including:
- Relieving symptoms:
Repairing an inguinal hernia can alleviate symptoms such as pain, discomfort, and a noticeable bulge or lump in the groin. - Preventing complications:
Untreated inguinal hernias can lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, strangulation, and tissue damage. Repairing the hernia can prevent these complications from occurring. - Minimally invasive approach:
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure that uses small incisions and a camera to repair the hernia, resulting in less pain and a shorter recovery time compared to open surgery. - Shorter recovery time:
With laparoscopic hernia repair, most patients are able to return to normal activities within a few days to a week, whereas open surgery may require several weeks of recovery time. - Low recurrence rate:
The use of surgical mesh in inguinal hernia repair has been shown to reduce the risk of the hernia recurring.
Surgery Procedure
An inguinal hernia is a condition where tissue or an organ protrudes through a weak point in the abdominal wall, typically near the groin area. The following is a general overview of the procedure for repairing an inguinal hernia:
- Preoperative preparation:
Before the surgery, the patient will be evaluated by a medical professional who will review their medical history and perform a physical exam. The patient may be required to undergo some tests such as blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies to ensure they are healthy enough for the procedure. - Anesthesia:
The patient will be given anesthesia to numb the area or to put them to sleep depending on the type of hernia repair. - Incision:
The surgeon will make an incision in the groin area over the hernia. - Reduction:
The hernia sac will be pushed back into the abdomen, and the contents of the sac (if any) will be reduced or pushed back as well. - Repair:
The surgeon will reinforce the weakened abdominal wall with a mesh patch or sutures to prevent the hernia from recurring. - Closure:
The incision is closed using sutures, staples or adhesive skin glue. - Postoperative care:
The patient will be monitored in the recovery room until the anesthesia wears off. Pain management, wound care, and physical activity restrictions will be discussed.
The procedure for repairing an inguinal hernia can be done as an open surgery or a laparoscopic surgery, and the specifics of the procedure will depend on the patient’s individual case and the surgeon’s preferred technique.
Frequently asked questions
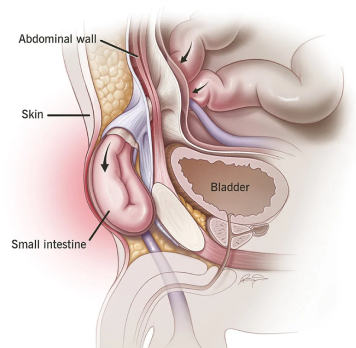
An inguinal hernia occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, causing a bulge or swelling in the groin area. While not necessarily life-threatening, inguinal hernias can cause discomfort, pain, and other complications if left untreated.
Some common symptoms of an inguinal hernia include a bulge or swelling in the groin or scrotum, pain or discomfort in the affected area, a feeling of weakness or pressure in the groin, and sometimes nausea or vomiting.
An inguinal hernia is located in the groin area, which is the area between the lower abdomen and the upper thigh on either side of the pubic bone.
Take charge of your health today. Schedule an appointment.
BOOK A SITTING