What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
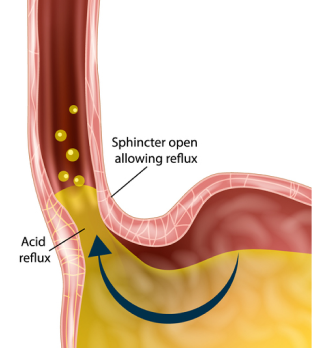
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disorder in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing inflammation and damage to the lining of the esophagus. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation of food or sour liquid.
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular ring that acts as a valve between the esophagus and the stomach, does not close properly or relaxes too frequently, allowing stomach acid to leak into the esophagus. Risk factors for GERD include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and certain medications.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) surgery Benefits
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) surgery, also known as antireflux surgery, is a treatment option for people with severe or persistent GERD who have not responded well to lifestyle changes or medication. The benefits of GERD surgery include:
- Improved quality of life:
GERD surgery can improve the quality of life for people with severe symptoms by reducing or eliminating the need for medications and providing long-term relief from symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. - Reduced risk of complications:
GERD can cause complications such as esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and esophageal cancer. Surgery can reduce the risk of these complications by improving the function of the lower esophageal sphincter and preventing acid reflux. - Reduced dependence on medications:
While medication can be effective in managing GERD symptoms, long-term use can have side effects and may not provide complete relief. Surgery can reduce the need for medication and its associated risks. - Faster recovery:
Most GERD surgeries are minimally invasive procedures that require only a few small incisions. This can result in a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) surgery Procedure
GERD treatment aims to cut down on the amount of reflux or lessen damage to the lining of the esophagus from refluxed materials. There are several surgical procedures used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), including:
- Nissen fundoplication:
This is the most common type of GERD surgery. It involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach around the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to strengthen the valve and prevent acid reflux. This procedure can be done through open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. - Toupet fundoplication:
This is a modified version of the Nissen fundoplication in which only the back part of the stomach is wrapped around the LES. This may be used in cases where the full wrap of the Nissen procedure is not necessary. - Linx device:
This is a small, flexible band of magnets that is placed around the LES. The magnetic attraction between the beads helps to keep the LES closed, preventing acid reflux. This procedure is done laparoscopically. - Endoluminal gastroplication:
This procedure involves using a device inserted through the mouth to create folds in the tissue of the LES, which helps to tighten the valve and prevent acid reflux. This procedure is done under sedation or general anesthesia. - Stretta procedure:
This is a non-surgical procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to create small burns in the tissue of the LES. The scarring that results from the burns helps to tighten the valve and prevent acid reflux.
The Nissen fundoplication procedure, which is the most common type of GERD surgery, typically takes about two to three hours to complete. The Toupet fundoplication and Linx device procedures may take slightly less time. Non-surgical procedures like the Stretta procedure and endoluminal gastroplication can usually be completed in under an hour.
Frequently asked questions
Paraesophageal hernias can cause symptoms such as: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), Feeling of fullness or discomfort in the, chest or upper abdomen after eating, Heartburn or acid reflux, Chest pain, Shortness of breath, Vomiting blood or passing dark, tarry stools (a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding), Anemia (a low red blood cell count)
GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) can be treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Prescription-strength proton pump inhibitors, such as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), omeprazole (Prilosec), pantoprazole (Protonix), rabeprazole (Aciphex), and dexlansoprazole (Dexilant), are commonly used for GERD treatment.
The worst foods for acid reflux list includes: Fatty or fried foods, Citrus fruits, Spicy foods, Coffee and tea, Carbonated beverages, Alcohol, and Chocolate.
Take charge of your health today. Schedule an appointment.
BOOK A SITTING