What is Laparoscopic Appendectomy?
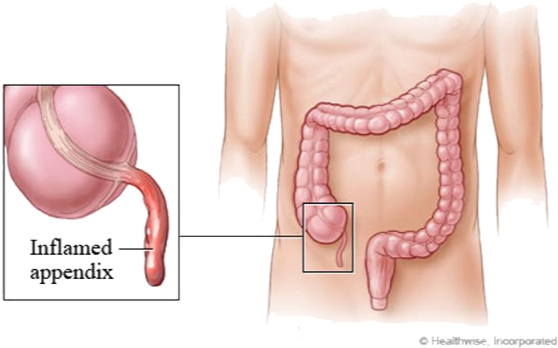
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove an inflamed appendix through small incisions in the abdomen. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped organ located in the lower right side of the abdomen. It is usually removed when it becomes inflamed due to a condition called appendicitis.
During a surgery, the surgeon makes a few small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope, which is a thin, lighted tube with a camera attached, and other small surgical instruments. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to visualize the appendix and surrounding tissue on a video monitor, and then removes the inflamed appendix through one of the small incisions.
Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic appendectomy typically results in less pain, shorter hospital stay, and quicker recovery time. However, not all cases of appendicitis are suitable for laparoscopic surgery, and sometimes open surgery may be necessary.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy surgery Benefits
Laparoscopic Surgery has several benefits compared to traditional open surgery for removing an inflamed appendix. Some of the key benefits of laparoscopic appendectomy include:
- Smaller incisions:
Laparoscopic appendectomy requires only a few small incisions in the abdomen, which are typically less than an inch long. This results in less scarring and a faster recovery time. - Reduced pain and discomfort:
Smaller incisions mean less pain and discomfort after surgery. Patients who undergo laparoscopic appendectomy may require less pain medication and can often resume normal activities sooner than those who have open surgery. - Quicker recovery time:
Laparoscopic appendectomy is typically associated with a shorter hospital stay and a quicker recovery time compared to open surgery. Many patients can return to work or school within a week or two of surgery. - Lower risk of complications:
Laparoscopic appendectomy is associated with a lower risk of complications, such as infection and hernia formation, compared to open surgery. - Better cosmetic outcome:
Because laparoscopic appendectomy requires smaller incisions, the resulting scars are often less noticeable than those from open surgery.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy Procedure
The procedure is commonly used to treat appendicitis, which is an inflammation of the appendix. Here are the steps involved in the laparoscopic appendectomy procedure:
- Anesthesia:
The patient is given general anesthesia, which means that they are unconscious during the procedure. - Incisions:
The surgeon makes a few small incisions in the abdomen, typically three or four. Carbon dioxide gas is then used to inflate the abdomen, which creates space for the surgeon to work. - Insertion of laparoscope:
The surgeon inserts a laparoscope, which is a thin, lighted tube with a camera attached, into one of the incisions. The laparoscope allows the surgeon to see the appendix and surrounding tissue on a video monitor. - Identification of appendix:
The surgeon identifies the inflamed appendix and determines the best way to remove it. - Dissection and removal of appendix:
The surgeon uses small surgical instruments inserted through the other incisions to dissect the appendix from surrounding tissue and remove it. The appendix is then placed in a specimen bag and removed from the body. - Closure of incisions:
The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue. A sterile dressing is then applied. - Recovery:
The patient is monitored in a recovery room for a period of time before being transferred to a hospital room. They may be given pain medication, antibiotics, and fluids as needed. The patient can usually return home within a day or two of surgery.
The duration of a procedure can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes around 30-60 minutes to complete.
Frequently asked questions
Laparoscopic appendectomy is generally considered a minimally invasive surgical procedure and is associated with less pain and a quicker recovery time compared to open appendectomy. However, it is still a surgical procedure and some level of pain and discomfort can be expected.
The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope, which is a long, thin instrument with a camera and light at the end, along with other surgical instruments to remove the appendix.
Full recovery time of laparoscopic appendectomy is quite short as compare to the open surgical procedure of appendectomy and that is around 1 week.
Take charge of your health today. Schedule an appointment.
BOOK A SITTING